Event Loop - Trái tim của JavaScript bất đồng bộ
Event Loop là một trong những khái niệm quan trọng nhất để hiểu cách JavaScript xử lý các tác vụ bất đồng bộ. Mặc dù JavaScript là ngôn ngữ single-threaded, nhưng nhờ Event Loop, nó có thể thực hiện các tác vụ non-blocking và có vẻ như “đa luồng”. Hãy cùng tìm hiểu chi tiết!
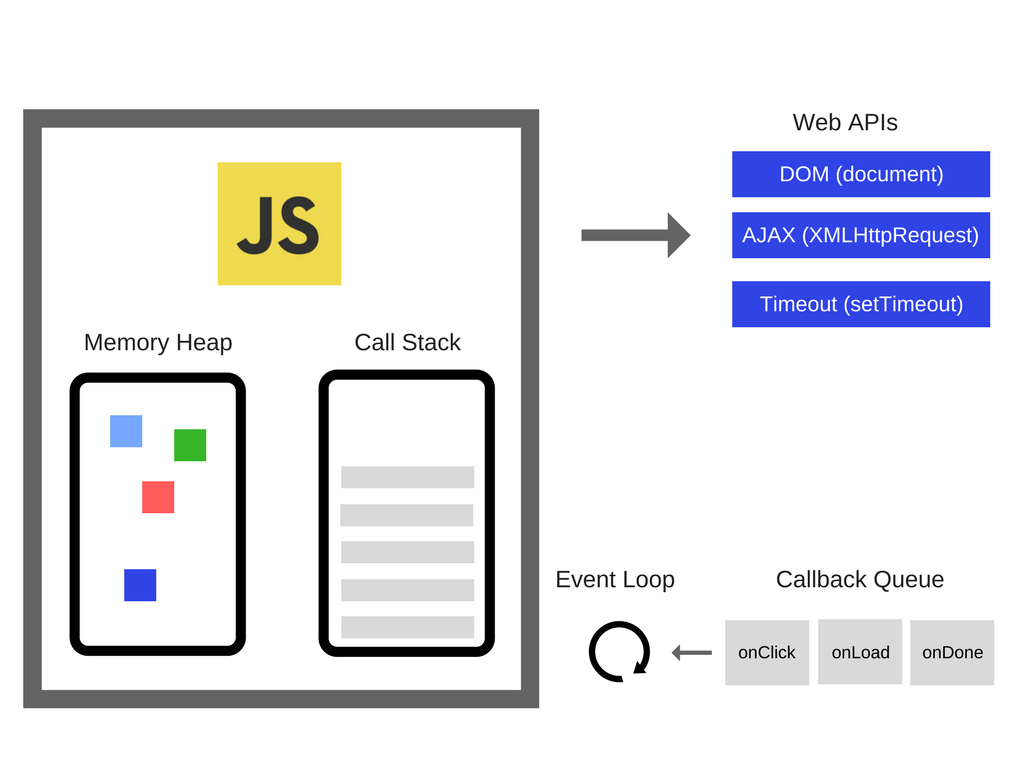
JavaScript Runtime Environment
Trước khi tìm hiểu Event Loop, chúng ta cần hiểu môi trường runtime của JavaScript:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ JavaScript Runtime │
├─────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ │
│ │ Call Stack │ │ Web APIs │ │
│ │ │ │ - setTimeout │ │
│ │ main() │ │ - DOM Events │ │
│ │ foo() │ │ - HTTP Req │ │
│ │ bar() │ │ - Promise │ │
│ └─────────────────┘ └───────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ │
│ │ Callback Queue │ │ Microtask │ │
│ │ (Task Queue) │ │ Queue │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────────┘ └───────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────┐ │
│ │ Event Loop │ │
│ └─────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘Call Stack - Ngăn xếp cuộc gọi
Call Stack là nơi JavaScript theo dõi các function calls. Nó hoạt động theo nguyên tắc LIFO (Last In, First Out).
Cách hoạt động của Call Stack
function first() {
console.log("First function start");
second();
console.log("First function end");
}
function second() {
console.log("Second function start");
third();
console.log("Second function end");
}
function third() {
console.log("Third function");
}
// Execution
console.log("Script start");
first();
console.log("Script end");
/* Call Stack timeline:
1. [main]
2. [main, console.log]
3. [main]
4. [main, first]
5. [main, first, console.log]
6. [main, first]
7. [main, first, second]
8. [main, first, second, console.log]
9. [main, first, second]
10. [main, first, second, third]
11. [main, first, second, third, console.log]
12. [main, first, second, third]
13. [main, first, second]
14. [main, first, second, console.log]
15. [main, first, second]
16. [main, first]
17. [main, first, console.log]
18. [main, first]
19. [main]
20. [main, console.log]
21. [main]
22. []
*/Stack Overflow
// ❌ Infinite recursion - Stack Overflow
function recursiveFunction() {
console.log("Calling myself");
recursiveFunction(); // No base case!
}
// recursiveFunction(); // RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
// ✅ Proper recursion với base case
function countDown(n) {
if (n <= 0) return; // Base case
console.log(n);
countDown(n - 1);
}
countDown(5); // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1Web APIs - Môi trường bên ngoài
Web APIs không phải part của JavaScript engine mà được cung cấp bởi browser hoặc Node.js runtime.
Browser Web APIs
// DOM API
document.getElementById('button').addEventListener('click', function() {
console.log('Button clicked!');
});
// Timer APIs
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Timer expired!');
}, 1000);
setInterval(() => {
console.log('Interval tick');
}, 2000);
// HTTP API
fetch('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
// Geolocation API
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(
position => console.log(position),
error => console.error(error)
);Node.js APIs
// File System API
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('file.txt', 'utf8', (err, data) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(data);
});
// HTTP Server API
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Hello World!');
});
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running on port 3000');
});Event Loop - Vòng lặp sự kiện
Event Loop có một công việc đơn giản: kiểm tra Call Stack và Task Queues, và di chuyển tasks từ queues vào stack khi stack trống.
Event Loop Algorithm
// Simplified Event Loop algorithm
while (true) {
// 1. Execute all microtasks
while (microtaskQueue.length > 0) {
const microtask = microtaskQueue.shift();
execute(microtask);
}
// 2. Execute one macrotask (if any)
if (callStack.isEmpty() && macrotaskQueue.length > 0) {
const macrotask = macrotaskQueue.shift();
execute(macrotask);
}
// 3. Update rendering (if needed)
updateRendering();
}Callback Queue (Task Queue)
Callback Queue chứa các macrotasks - tasks được schedule bởi Web APIs.
console.log('1'); // Synchronous
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('2'); // Macrotask - vào Callback Queue
}, 0);
console.log('3'); // Synchronous
// Output: 1, 3, 2
// Mặc dù timeout = 0, callback vẫn phải đợi Call Stack trốngVí dụ phức tạp hơn
console.log('Start');
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout 1'), 0);
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout 2'), 0);
console.log('End');
/* Timeline:
1. Call Stack: [console.log] → "Start"
2. Call Stack: [setTimeout] → Web API handles timer
3. Call Stack: [setTimeout] → Web API handles timer
4. Call Stack: [console.log] → "End"
5. Call Stack: [] → Event Loop moves callback from queue
6. Call Stack: [callback] → "Timeout 1"
7. Call Stack: [] → Event Loop moves next callback
8. Call Stack: [callback] → "Timeout 2"
Output: Start, End, Timeout 1, Timeout 2
*/Microtask Queue - Hàng đợi ưu tiên
Microtask Queue có độ ưu tiên cao hơn Callback Queue. Các microtasks bao gồm:
- Promise callbacks (
.then(),.catch(),.finally()) queueMicrotask()MutationObservercallbacks
console.log('1');
setTimeout(() => console.log('2'), 0); // Macrotask
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('3')); // Microtask
console.log('4');
// Output: 1, 4, 3, 2
// Microtask (Promise) được execute trước Macrotask (setTimeout)Ví dụ chi tiết về priorities
console.log('=== Start ===');
// Macrotasks
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout 1'), 0);
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout 2'), 0);
// Microtasks
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('Promise 1'));
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('Promise 2'));
// More microtasks
queueMicrotask(() => console.log('Microtask 1'));
queueMicrotask(() => console.log('Microtask 2'));
console.log('=== End ===');
/* Output:
=== Start ===
=== End ===
Promise 1
Promise 2
Microtask 1
Microtask 2
Timeout 1
Timeout 2
*/Ví dụ thực tế với Event Loop
Ví dụ 1: User Interface Updates
// ❌ Blocking UI - Bad practice
function heavyCalculation() {
console.log('Heavy calculation start');
// Simulate heavy work
const start = Date.now();
while (Date.now() - start < 3000) {
// Blocking for 3 seconds
}
console.log('Heavy calculation end');
}
// Button click sẽ freeze UI
document.getElementById('heavy-btn').addEventListener('click', heavyCalculation);
// ✅ Non-blocking UI - Good practice
function heavyCalculationAsync() {
console.log('Async calculation start');
function chunk(index = 0) {
const chunkSize = 1000000;
let count = 0;
// Do work in small chunks
while (count < chunkSize && index < 10000000) {
index++;
count++;
}
if (index < 10000000) {
// Schedule next chunk
setTimeout(() => chunk(index), 0);
} else {
console.log('Async calculation end');
}
}
chunk();
}Ví dụ 2: API Calls với Error Handling
function fetchUserData(userId) {
console.log(`Fetching user ${userId}...`);
return fetch(`/api/users/${userId}`)
.then(response => {
console.log('Response received');
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP ${response.status}`);
}
return response.json();
})
.then(userData => {
console.log('User data parsed');
return userData;
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Fetch error:', error);
throw error;
});
}
// Usage
console.log('App start');
fetchUserData(123)
.then(user => {
console.log('Got user:', user.name);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('Failed to get user');
});
console.log('App continues...');
/* Timeline:
1. "App start"
2. "Fetching user 123..."
3. "App continues..."
4. [HTTP request completes] → Microtask scheduled
5. "Response received"
6. "User data parsed"
7. "Got user: [name]"
*/Ví dụ 3: Multiple Async Operations
async function demonstrateAsyncFlow() {
console.log('=== Async Demo Start ===');
// Immediate microtask
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('Immediate Promise'));
// Delayed macrotask
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout 0ms'), 0);
// Another immediate microtask
queueMicrotask(() => console.log('Immediate Microtask'));
// Await (creates microtask when resolves)
await Promise.resolve();
console.log('After await');
// Nested async operations
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Nested Timeout');
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('Nested Promise'));
setTimeout(() => console.log('Deeply Nested Timeout'), 0);
}, 10);
console.log('=== Async Demo End ===');
}
demonstrateAsyncFlow();
/* Output:
=== Async Demo Start ===
=== Async Demo End ===
Immediate Promise
Immediate Microtask
After await
Timeout 0ms
Nested Timeout
Nested Promise
Deeply Nested Timeout
*/Debugging Event Loop
Visualization Tool
class EventLoopVisualizer {
constructor() {
this.callStack = [];
this.macrotasks = [];
this.microtasks = [];
this.step = 0;
}
log(message, type = 'sync') {
this.step++;
console.log(`Step ${this.step}: [${type.toUpperCase()}] ${message}`);
this.printState();
}
addMacrotask(task) {
this.macrotasks.push(task);
console.log(`➕ Added macrotask: ${task}`);
}
addMicrotask(task) {
this.microtasks.push(task);
console.log(`⚡ Added microtask: ${task}`);
}
printState() {
console.log(`📚 Call Stack: [${this.callStack.join(', ')}]`);
console.log(`⏰ Macrotasks: [${this.macrotasks.join(', ')}]`);
console.log(`⚡ Microtasks: [${this.microtasks.join(', ')}]`);
console.log('─'.repeat(50));
}
}
// Usage
const visualizer = new EventLoopVisualizer();
visualizer.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => visualizer.log('Timeout executed', 'macro'), 0);
visualizer.addMacrotask('setTimeout callback');
Promise.resolve().then(() => visualizer.log('Promise executed', 'micro'));
visualizer.addMicrotask('Promise.then callback');
visualizer.log('Script end');Performance Monitoring
function measureEventLoopLag() {
const start = process.hrtime.bigint();
setImmediate(() => {
const lag = process.hrtime.bigint() - start;
const lagMs = Number(lag) / 1000000; // Convert to milliseconds
console.log(`Event Loop Lag: ${lagMs.toFixed(2)}ms`);
if (lagMs > 10) {
console.warn('⚠️ High event loop lag detected!');
}
});
}
// Monitor continuously
setInterval(measureEventLoopLag, 1000);Common Patterns và Anti-patterns
Pattern 1: Microtask Batching
// ✅ Batching updates using microtasks
class StateManager {
constructor() {
this.state = {};
this.pendingUpdates = new Set();
this.isUpdateScheduled = false;
}
setState(key, value) {
this.state[key] = value;
this.pendingUpdates.add(key);
if (!this.isUpdateScheduled) {
this.isUpdateScheduled = true;
// Batch all synchronous updates
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.flushUpdates();
this.isUpdateScheduled = false;
});
}
}
flushUpdates() {
console.log('Flushing updates:', [...this.pendingUpdates]);
// Notify observers
this.pendingUpdates.forEach(key => {
this.notifyObservers(key, this.state[key]);
});
this.pendingUpdates.clear();
}
notifyObservers(key, value) {
console.log(`State changed: ${key} = ${value}`);
}
}
const state = new StateManager();
// These will be batched together
state.setState('user', 'John');
state.setState('age', 30);
state.setState('city', 'New York');
console.log('All updates scheduled');Anti-pattern 1: Microtask Starvation
// ❌ Microtask starvation - blocks macrotasks
function createMicrotaskStarvation() {
function addMicrotask() {
queueMicrotask(() => {
console.log('Microtask executed');
addMicrotask(); // Infinite microtasks!
});
}
addMicrotask();
// This timeout will NEVER execute
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout - will never run'), 0);
}
// ✅ Proper way - yield to macrotasks
function createProperAsyncLoop() {
function addMicrotask(count = 0) {
if (count >= 5) return; // Limit microtasks
queueMicrotask(() => {
console.log(`Microtask ${count}`);
// Use setTimeout to yield to macrotasks
setTimeout(() => addMicrotask(count + 1), 0);
});
}
addMicrotask();
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout executed'), 0);
}
createProperAsyncLoop();Pattern 2: Yielding Control
// ✅ Yielding control for better UX
async function processLargeDataset(data) {
const batchSize = 1000;
const results = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i += batchSize) {
const batch = data.slice(i, i + batchSize);
// Process batch
const batchResults = batch.map(item => processItem(item));
results.push(...batchResults);
// Yield control every batch
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 0));
// Update progress
const progress = Math.floor((i / data.length) * 100);
updateProgress(progress);
}
return results;
}
function processItem(item) {
// Simulate processing
return item * 2;
}
function updateProgress(progress) {
console.log(`Progress: ${progress}%`);
}
// Usage
const largeData = Array.from({ length: 10000 }, (_, i) => i);
processLargeDataset(largeData);Performance Optimization
1. Avoid Blocking the Main Thread
// ❌ Blocking operation
function syncHeavyWork(data) {
return data.map(item => {
// Heavy computation
let result = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
result += Math.random() * item;
}
return result;
});
}
// ✅ Non-blocking with chunks
async function asyncHeavyWork(data, chunkSize = 100) {
const results = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i += chunkSize) {
const chunk = data.slice(i, i + chunkSize);
const chunkResults = chunk.map(item => {
let result = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) {
result += Math.random() * item;
}
return result;
});
results.push(...chunkResults);
// Yield control
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 0));
}
return results;
}2. Optimize Promise Chains
// ❌ Sequential async operations
async function slowSequential() {
const user = await fetchUser();
const posts = await fetchPosts();
const comments = await fetchComments();
return { user, posts, comments };
}
// ✅ Parallel async operations
async function fastParallel() {
const [user, posts, comments] = await Promise.all([
fetchUser(),
fetchPosts(),
fetchComments()
]);
return { user, posts, comments };
}
// Mock functions
async function fetchUser() {
return new Promise(resolve =>
setTimeout(() => resolve({ id: 1, name: 'John' }), 100)
);
}
async function fetchPosts() {
return new Promise(resolve =>
setTimeout(() => resolve([{ id: 1, title: 'Post 1' }]), 100)
);
}
async function fetchComments() {
return new Promise(resolve =>
setTimeout(() => resolve([{ id: 1, text: 'Comment 1' }]), 100)
);
}Browser vs Node.js Event Loop
Browser Event Loop
// Browser-specific APIs
console.log('1');
// macrotask
setTimeout(() => console.log('2'), 0);
// microtask
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('3'));
// Animation frame (special macrotask)
requestAnimationFrame(() => console.log('4'));
// microtask
queueMicrotask(() => console.log('5'));
console.log('6');
// Browser output: 1, 6, 3, 5, 2, 4
// (requestAnimationFrame runs after timeout in this case)Node.js Event Loop Phases
// Node.js has different phases
const fs = require('fs');
console.log('1');
// Timer phase
setTimeout(() => console.log('2'), 0);
setImmediate(() => console.log('3')); // Check phase
// I/O phase
fs.readFile(__filename, () => console.log('4'));
// microtask
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('5'));
process.nextTick(() => console.log('6')); // Highest priority
console.log('7');
// Node.js output: 1, 7, 6, 5, 2, 3, 4
// (process.nextTick has highest priority)Event Loop Best Practices
1. Monitor Event Loop Health
// Check event loop lag
function checkEventLoopHealth() {
const start = process.hrtime();
setImmediate(() => {
const delta = process.hrtime(start);
const nanosec = delta[0] * 1e9 + delta[1];
const millisec = nanosec / 1e6;
console.log(`Event loop lag: ${millisec.toFixed(2)}ms`);
if (millisec > 10) {
console.warn('Event loop is lagging!');
}
});
}
setInterval(checkEventLoopHealth, 1000);2. Use Appropriate Task Types
// ✅ Use microtasks for state updates
function updateState(newState) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
Object.assign(this.state, newState);
this.render();
});
}
// ✅ Use macrotasks for heavy work
function processData(data) {
setTimeout(() => {
// Heavy processing
const result = heavyComputation(data);
displayResult(result);
}, 0);
}
// ✅ Use requestAnimationFrame for animations
function animateElement(element) {
let start = null;
function animate(timestamp) {
if (!start) start = timestamp;
const progress = timestamp - start;
element.style.left = Math.min(progress / 10, 200) + 'px';
if (progress < 2000) {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
}
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}3. Error Handling trong Async Code
// ✅ Proper error handling
async function robustAsyncFunction() {
try {
const data = await fetchData();
const processed = await processData(data);
return processed;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Async operation failed:', error);
// Don't let errors crash the event loop
return { error: error.message };
}
}
// ✅ Global error handlers
window.addEventListener('unhandledrejection', (event) => {
console.error('Unhandled promise rejection:', event.reason);
event.preventDefault(); // Prevent default browser behavior
});
process.on('uncaughtException', (error) => {
console.error('Uncaught exception:', error);
// Graceful shutdown
process.exit(1);
});Kết luận
Event Loop là foundation của JavaScript’s concurrency model và hiểu rõ nó là chìa khóa để viết code hiệu quả:
🎯 Key Takeaways
- JavaScript is single-threaded nhưng có thể non-blocking nhờ Event Loop
- Microtasks > Macrotasks - Priority matters
- Call Stack phải empty trước khi Event Loop di chuyển tasks
- Web APIs handle async operations bên ngoài main thread
- Understanding timing giúp debug và optimize performance
🚀 Performance Tips
- Avoid blocking the main thread với heavy computations
- Batch updates sử dụng microtasks
- Yield control với setTimeout(0) hoặc await
- Monitor event loop lag trong production
- Use appropriate task types cho different scenarios
⚡ Common Patterns
- Debouncing/Throttling với timers
- Batching state updates với microtasks
- Chunking heavy work để maintain responsiveness
- Parallel async operations với Promise.all()
- Graceful error handling để prevent crashes
TIPMaster Event Loop sẽ giúp bạn viết JavaScript applications responsive, efficient và scalable!
Event Loop knowledge là essential để understand và debug complex async behaviors, optimize performance, và build better user experiences.