Debounce và Throttle trong JavaScript – Làm mượt UI & tối ưu hiệu suất
6 phút
Khi xử lý events như typing, scrolling, resizing… nếu không kiểm soát tần suất, ứng dụng có thể bị lag hoặc crash. Debounce và Throttle là 2 kỹ thuật quan trọng để giải quyết vấn đề này.
Vấn đề: Event quá nhiều lần ⚡
Ví dụ search input không tối ưu
// ❌ Gọi API mỗi lần gõ phím - Tệ!
const searchInput = document.getElementById('search');
searchInput.addEventListener('input', (e) => {
searchAPI(e.target.value); // Gọi API liên tục!
});
// Gõ "Hello" = 5 API calls: H, He, Hel, Hell, Hello
// Tốn bandwidth, lag UI, server quá tải 💸Ví dụ scroll event không tối ưu
// ❌ Tính toán mỗi lần scroll - Lag!
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
updateProgressBar(); // Chạy hàng trăm lần/giây!
checkElementInView();
animateElements();
});
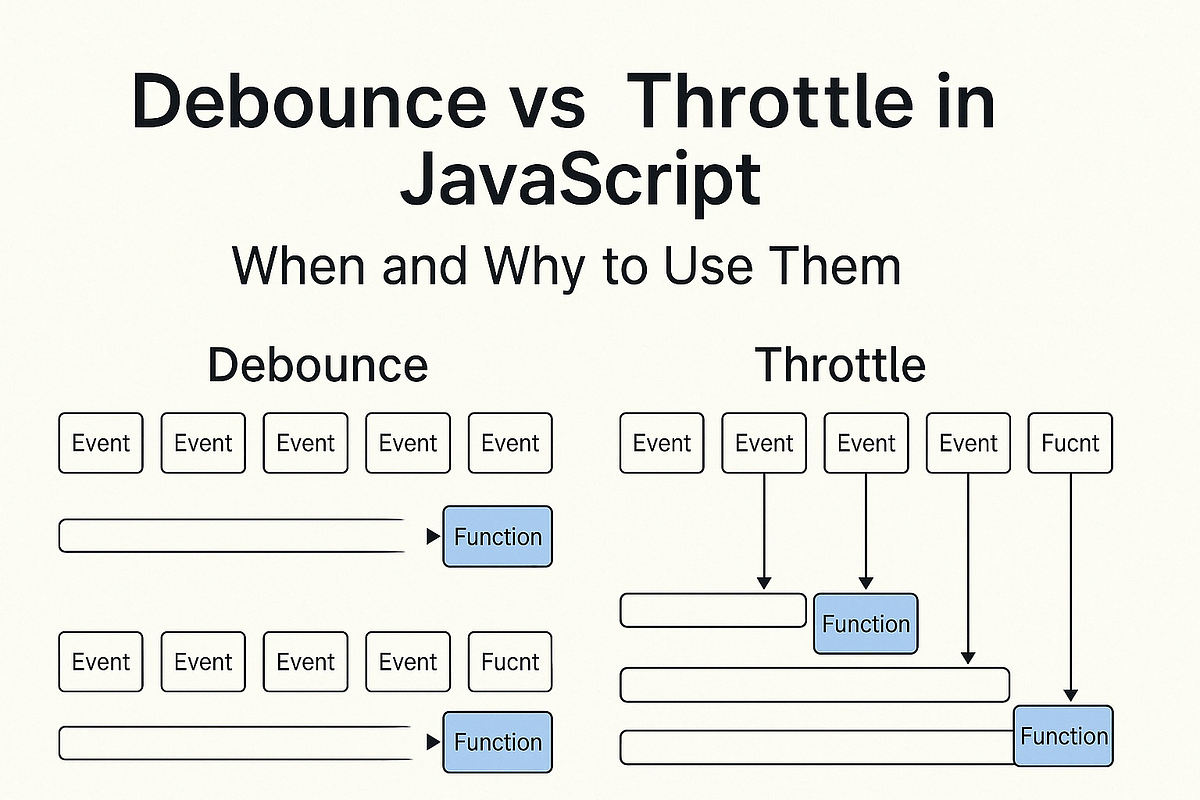
// Scroll 1 giây = 60-120 lần chạy → UI lag 🐌Debounce: “Chờ người dùng ngừng” ⏳
Debounce chỉ thực thi sau khi user ngừng trigger event trong khoảng thời gian nhất định.
Tự code Debounce function
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timeoutId;
return function(...args) {
// Hủy timeout cũ (nếu có)
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
// Đặt timeout mới
timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(this, args);
}, delay);
};
}Ví dụ: Search input với Debounce
// ✅ Chỉ gọi API khi user ngừng gõ 300ms
const searchInput = document.getElementById('search');
const debouncedSearch = debounce((query) => {
console.log('Searching for:', query);
searchAPI(query);
}, 300);
searchInput.addEventListener('input', (e) => {
debouncedSearch(e.target.value);
});
// Gõ "Hello" nhanh = 1 API call duy nhất ✅Ví dụ: Window resize với Debounce
// ✅ Chỉ recalculate khi user ngừng resize
const debouncedResize = debounce(() => {
console.log('Window resized!');
recalculateLayout();
updateChartSize();
}, 250);
window.addEventListener('resize', debouncedResize);Throttle: “Giới hạn tần suất” 🎛️
Throttle giới hạn function chỉ chạy tối đa 1 lần trong khoảng thời gian nhất định.
Tự code Throttle function
function throttle(func, delay) {
let lastCall = 0;
return function(...args) {
const now = Date.now();
// Chỉ chạy nếu đã đủ thời gian delay
if (now - lastCall >= delay) {
lastCall = now;
func.apply(this, args);
}
};
}Ví dụ: Scroll event với Throttle
// ✅ Chỉ update 1 lần/16ms (≈60fps)
const throttledScroll = throttle(() => {
const scrollPercent = (window.scrollY / (document.body.scrollHeight - window.innerHeight)) * 100;
updateProgressBar(scrollPercent);
// Check lazy loading
checkLazyImages();
}, 16);
window.addEventListener('scroll', throttledScroll);Ví dụ: Button click protection
// ✅ Chống spam click
const submitButton = document.getElementById('submit');
const throttledSubmit = throttle(() => {
console.log('Submitting form...');
submitForm();
}, 1000);
submitButton.addEventListener('click', throttledSubmit);
// Click liên tục = chỉ submit 1 lần/giâyDebounce vs Throttle: Khi nào dùng gì? 🤔
| Use Case | Debounce | Throttle | Lý do |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search input | ✅ | ❌ | Chờ user gõ xong |
| Form validation | ✅ | ❌ | Validate khi ngừng nhập |
| Save draft | ✅ | ❌ | Save khi ngừng gõ |
| Scroll progress | ❌ | ✅ | Update liên tục nhưng giới hạn |
| Mouse move animation | ❌ | ✅ | Animation mượt |
| API rate limiting | ❌ | ✅ | Giới hạn request/s |
| Resize handler | ✅ | ❌ | Recalculate khi ngừng resize |
| Button spam protection | ❌ | ✅ | Giới hạn click rate |
Minh họa trực quan
// Event timeline: ||||||||||||||||||||
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 (giây)
// Debounce (300ms): Chỉ chạy sau khi ngừng 300ms
// Execute: ❌❌❌❌❌❌❌❌❌✅ (cuối cùng)
// Throttle (1s): Chạy tối đa 1 lần/giây
// Execute: ✅❌❌❌❌✅❌❌❌❌ (định kỳ)Ví dụ thực tế: Search với Debounce 🔍
HTML
<div class="search-container">
<input
type="text"
id="search-input"
placeholder="Tìm kiếm sản phẩm..."
>
<div id="search-results"></div>
<div id="search-stats"></div>
</div>JavaScript
// Mock API
async function searchAPI(query) {
const response = await fetch(`/api/search?q=${query}`);
return response.json();
}
// Debounce function
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timeoutId;
return function(...args) {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = setTimeout(() => func.apply(this, args), delay);
};
}
// Search handler
let searchCount = 0;
const handleSearch = async (query) => {
if (!query.trim()) {
document.getElementById('search-results').innerHTML = '';
return;
}
searchCount++;
document.getElementById('search-stats').textContent =
`Tìm kiếm lần thứ ${searchCount}: "${query}"`;
try {
const results = await searchAPI(query);
displayResults(results);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Search error:', error);
}
};
// Apply debounce
const debouncedSearch = debounce(handleSearch, 300);
// Event listener
document.getElementById('search-input').addEventListener('input', (e) => {
debouncedSearch(e.target.value);
});
function displayResults(results) {
const container = document.getElementById('search-results');
container.innerHTML = results.map(item =>
`<div class="result-item">${item.name}</div>`
).join('');
}
// So sánh: Không dùng debounce
// document.getElementById('search-input').addEventListener('input', (e) => {
// handleSearch(e.target.value); // Gọi API mỗi ký tự!
// });Ví dụ thực tế: Scroll với Throttle 📜
HTML
<div class="progress-container">
<div class="progress-bar" id="progress-bar"></div>
</div>
<div class="content">
<!-- Nội dung dài... -->
</div>
<div class="scroll-stats" id="scroll-stats"></div>CSS
.progress-container {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 4px;
background: #f0f0f0;
z-index: 1000;
}
.progress-bar {
height: 100%;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #667eea 0%, #764ba2 100%);
width: 0%;
transition: width 0.1s ease;
}JavaScript
// Throttle function
function throttle(func, delay) {
let lastCall = 0;
return function(...args) {
const now = Date.now();
if (now - lastCall >= delay) {
lastCall = now;
func.apply(this, args);
}
};
}
// Scroll handler
let scrollCount = 0;
const handleScroll = () => {
scrollCount++;
// Tính toán progress
const scrollTop = window.pageYOffset;
const docHeight = document.body.offsetHeight;
const winHeight = window.innerHeight;
const scrollPercent = (scrollTop / (docHeight - winHeight)) * 100;
// Update progress bar
document.getElementById('progress-bar').style.width = `${scrollPercent}%`;
// Update stats
document.getElementById('scroll-stats').textContent =
`Scroll events: ${scrollCount} | Progress: ${Math.round(scrollPercent)}%`;
// Lazy loading check (giả lập)
checkLazyImages();
};
// Apply throttle
const throttledScroll = throttle(handleScroll, 16); // ~60fps
// Event listener
window.addEventListener('scroll', throttledScroll);
function checkLazyImages() {
// Logic lazy loading images
// console.log('Checking lazy images...');
}
// So sánh: Không dùng throttle
// window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll); // Chạy hàng trăm lần!Advanced: Throttle với leading/trailing options 🎯
function throttleAdvanced(func, delay, options = {}) {
const { leading = true, trailing = true } = options;
let timeoutId, lastCall = 0, lastArgs;
return function(...args) {
const now = Date.now();
// First call
if (!lastCall && leading === false) {
lastCall = now;
}
const remaining = delay - (now - lastCall);
lastArgs = args;
if (remaining <= 0 || remaining > delay) {
if (timeoutId) {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = null;
}
lastCall = now;
func.apply(this, args);
} else if (!timeoutId && trailing !== false) {
timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
lastCall = leading === false ? 0 : Date.now();
timeoutId = null;
func.apply(this, lastArgs);
}, remaining);
}
};
}
// Sử dụng
const advancedThrottle = throttleAdvanced(handleScroll, 100, {
leading: true, // Chạy ngay lập tức
trailing: false // Không chạy cuối
});Performance Tips 🚀
1. Chọn delay phù hợp
// Search input: 300-500ms (UX tốt)
const searchDebounce = debounce(searchAPI, 300);
// Form validation: 500ms (ít spam)
const validateDebounce = debounce(validateForm, 500);
// Scroll: 16ms (60fps smooth)
const scrollThrottle = throttle(handleScroll, 16);
// Resize: 250ms (đủ nhanh)
const resizeDebounce = debounce(handleResize, 250);2. Cleanup khi component unmount
class SearchComponent {
constructor() {
this.debouncedSearch = debounce(this.search.bind(this), 300);
this.element.addEventListener('input', this.debouncedSearch);
}
destroy() {
// ✅ Cleanup để tránh memory leak
this.element.removeEventListener('input', this.debouncedSearch);
}
search(query) {
// API call
}
}3. Sử dụng thư viện
// Lodash - Production ready
import { debounce, throttle } from 'lodash';
const debouncedFn = debounce(myFunction, 300);
const throttledFn = throttle(myFunction, 100);
// Hoặc lightweight alternative
npm install just-debounce-it just-throttleKết luận 📋
| Kỹ thuật | Khi nào dùng | Ví dụ | Lợi ích |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debounce | Chờ user hoàn thành action | Search, resize, validation | Giảm API calls, UX tốt |
| Throttle | Giới hạn tần suất execution | Scroll, mouse move, button spam | Performance ổn định |
Key takeaways:
- 🔍 Search input → Debounce (300ms)
- 📜 Scroll events → Throttle (16ms)
- 🎯 Button protection → Throttle (1000ms)
- 📏 Window resize → Debounce (250ms)
Performance impact:
- ❌ Không tối ưu: 1000+ function calls/second
- ✅ Với Debounce/Throttle: 1-60 calls/second
- 🚀 Kết quả: UI mượt hơn, server ít tải hơn!
Áp dụng ngay vào project để cải thiện UX và performance! 🎉